Attackers' motivations showed significant changes in Q1 2018. Attacks targeting data increased to 36 percent of the total, compared to an average of 23 percent throughout 2017. However, criminals are as interested as ever in money: they pursued financial aims in more than half of cyberattacks.
Contents
Symbols used

Trends and forecasts
The world of cybercrime is constantly evolving. To reflect new attack vectors, certain adjustments in classification and grouping have been made in this edition. As always, Positive Technologies will share the information needed for a complete and up-todate picture of cybersecurity threats. The information in this report is taken from our company's in-house expertise and experience, industry research, and reporting from authoritative sources.
Noteworthy findings from the first quarter of 2018:
- The number of unique cyberincidents continued to grow, exceeding the equivalent year-ago period (Q1 2017) by 32 percent.
- Attacks aimed at obtaining data became more frequent. The target of such attacks was primarily personal information and account credentials. This information can be sold on the black market or used to pursue further attacks.
- Malware use was a factor in most attacks. Malware was often combined with other methods, such as social engineering and exploitation of web vulnerabilities.
- Spyware was the most common type of malware. Spyware allows obtaining personal data, corporate secrets, and account credentials, which grant access to sensitive internal systems.
- Individuals were a major target, with five out of six attacks making use of malware. Lack of antivirus protection, as well as careless downloading of files and opening of links, were primary contributing factors.
- Botnets took IoT devices by storm in 2017 to become more powerful than ever. The last day of winter marked the strongest-ever DDoS attack: 1.35 terabits per second.
Predictions:
- The number of unique cyberattacks will continue to rise.
- Attackers will refine existing vectors, particularly against government and finance targets.
- New malware will be dominated by spyware and cryptocurrency miners.
- Phishing campaigns will try to take advantage of interest in the upcoming 2018 FIFA World Cup.
- Large-scale DDoS attacks, including those with political motivations, will remain a fact of life.
Overview: motives, methods, targets
Attackers' motivations showed significant changes in Q1 2018. Attacks targeting data increased to 36 percent of the total, compared to an average of 23 percent throughout 2017. However, criminals are as interested as ever in money: they pursued financial aims in more than half of cyberattacks (53%). The main reason is that after a successful data theft, the attackers either continue their actions against the victim or its clients and partners (if the victim's client database was stolen, for example), or try to sell the information on the black market.

In 36 percent of cases, attackers succeeded in obtaining sensitive information. Not all information is equally attractive to attackers, however. In one third of cases (33%), this information consisted of personal data. In one quarter (28%), account credentials for services and systems were compromised. Naturally, such credentials are useful for pursuing attack vectors: attackers can access critical infrastructure including databases, workstations of senior management, and management servers (such as for web resources).

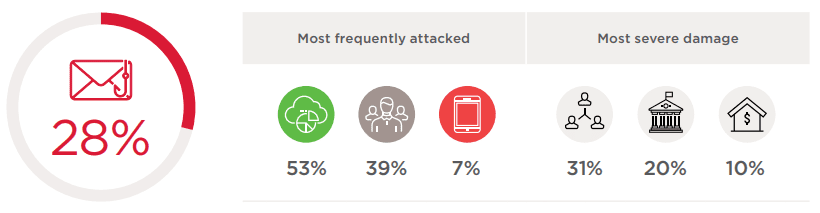
The largest share of attacks (28%) was directed at individuals. Government applications continued to draw more attacks, receiving 16 percent of the total in Q1 2018. Closer analysis of attacks against government, healthcare, finance, education, and individuals is given in the pages that follow. Large-scale cyberattacks affecting more than one industry (most often, malware outbreaks) have been placed in the "Multiple industries" category.

In Q1 2018, 52 percent of attacks were directed at infrastructure. Attacks on web resources decreased compared to 2017, falling from 26 to 19 percent of the total.
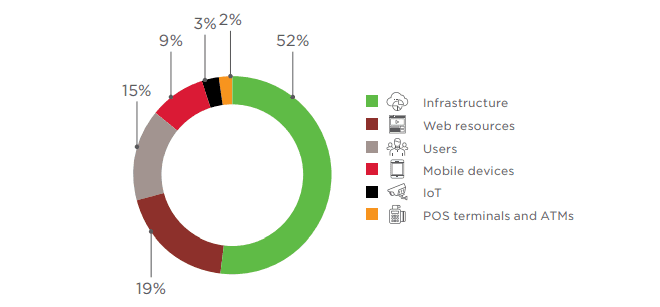
Criminals are tending to combine more methods in a single attack. For example, 18 percent of attacks featured both malware and social engineering; 5 percent involved exploitation of web vulnerabilities and malware. Later in this report, attack methods will be considered in detail, including the targets and industries most affected by each.

Per-industry classification of cyberincidents by motive, method, and target

Attack number
The number of unique cyberincidents in Q1 2018 increased by almost one third (32%) year-over-year. Most of the attacks occurred (or were discovered) in February and March, while in January, news was driven by large-scale malicious campaigns uncovered by antivirus vendors.


Attack methods
In this section, we will focus on each method in detail and look at which targets and victims were most affected.
Malware use

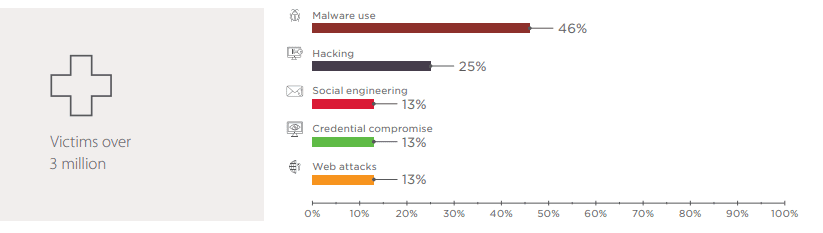
Malware is the rule, not the exception, in attacks. It is often combined with other methods such as social engineering or exploitation of web application vulnerabilities. In Q1 2018, malware was a component of 63 percent of unique cyberattacks.
Spyware (programs designed to obtain sensitive information, especially credentials, from an infected device) was used in 30 percent of cases. Cryptocurrency miners were spread in 23 percent of attacks. One of the "hits" of the quarter was WannaMine, which infected over 500,000 devices (primarily Windows servers) worldwide and used their CPU capacity to mine Monero cryptocurrency. WannaMine uses the EternalBlue (CVE-2017-0144) and EsteemAudit (CVE-2017-0176) vulnerabilities to spread.

In 38 percent of attacks using this method, the malware was sent to victims by email. Such malicious attachments were generally spyware, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), or ransomware. Depending on the type of attack, compromised websites and phishing pages push out cryptocurrency miners or spyware to targeted users.
Social engineering
Although social engineering can be combined with malware (such as on phishing sites that distribute malware), it is often effective all by itself. The first quarter included a wave of social engineering directed at the personal data of employees at American companies. At the beginning of each calendar year, U.S. employers must generate W-2 forms to indicate employee earnings. These forms contain a wealth of data, including full name, address, social security number, salary, and withheld taxes. Attackers masquerade as partners or IRS staff and ask company executives for W-2 forms for all employees.
ICOs remain popular among both investors and fraudsters. In early 2018, two similar attacks targeted Experty and Bee Token. In the case of Experty, attackers stole the company's list of email subscribers. Five days before the actual ICO start, the attackers sent out false emails announcing the start of sales. The emails indicated the Ethereum wallet of the attackers. Investors transferred funds to the wallet, to the tune of over $150,000. The same technique was used in the attack against Bee Token investors: attackers posed as the organizers to send emails and messages falsely announcing the start of sales.

Hacking

This category includes attacks involving exploitation of vulnerabilities in software and services, errors in protection mechanisms, and other flaws. In a typical targeted attack, hackers compromise the victim's infrastructure, obtain access to servers or computers that handle critical information, and infect these systems with spyware to stealthily exfiltrate this information.
Most of the attacks in this category could have been avoided by installing software updates in a timely manner. For example, web servers with out-of-date versions of Ruby on Rails, PHP, and Microsoft IIS ASP fell victim to RubyMiner. Attackers specially searched for web servers with p0f and then remotely ran code on the target system with any of six exploits. To hide its presence on infected systems, the malicious script was placed in the robots.txt file. A modified version of XMRig, a legitimate application for generating Monero cryptocurrency, was then downloaded and installed on the server.
Web attacks

Online stores can be a magnet for criminals. Vulnerabilities in these sites enable obtaining the card numbers needed for making a quick profit. In late 2017 and early 2018, purchasers of smartphones and accessories from the official OnePlus website fell victim to card fraud. Site vulnerabilities allowed criminals to inject a malicious script, which intercepted and transmitted purchasers' card information. Notably, users who had saved their payment information were not affected, since the attackers were unable to access the OnePlus database.
Web vulnerabilities are also useful for attackers interested in modifying site contents. These attacks can cause financial losses (when an ICO website is hacked to indicate a fraud ulent cryptocurrency wallet) as well as reputational damage.
In January 2018, attackers obtained access to the New Zealand Football official website and published material falsely claiming the resignation of CEO Andy Martin.

Credential compromise

To the frustration of security experts, the advice to use complex passwords and change them regularly frequently seems to go in one ear and out the other. As practice shows, weak passwords are often attackers' point of entry into target infrastructure.
Bruteforcing works against websites as well. For instance, more than 1,000 sites running the Magento CMS were compromised by hackers who bruteforced default passwords for administrative access. The sites were then used to:
- Intercept POST requests that contained credit card information.
- Embed cryptocurrency mining code, in order to generate cryptocurrency on visitors' computers for the benefit of the attackers.
- Redirect users to phishing sites.

In one incident investigated by the Positive Technologies Expert Security Center (PT ESC) in late 2017, attackers succeeded in penetrating a company's internal network by bruteforcing the password of the Internet-accessible RDP service on a company server. The attackers compromised a number of servers and, over the course of several days, obtained control of the company's internal resources while remaining unnoticed. The incident was discovered only after the attackers encrypted data on several servers (causing certain systems to fail) and demanded ransom. Often in such attacks, the victim's mail server is compromised as well. As a result, attackers can take advantage of the victim's good name in phishing messages to clients and partners. This incident underscores the hazards of using RDP and other Internet-accessible network interfaces, which often provide attackers with the ability to access the internal network of the victim.
DDoS

The last day of winter set a new record for the most powerful DDoS attack in history. The target was software code repository GitHub. Incoming traffic reached 1.35 terabits per second. The attack was repelled with the help of Akamai Prolexic, whose servers routed traffic coming to and from GitHub. After eight minutes, malicious packets were filtered out and the site resumed operating as normal.

Many cyberattacks are motivated by political events. On the day of presidential elections in Russia, a DDoS attack was made against the site of the Central Electoral Commission.
Victim categories
This section analyzes the threats encountered by each of the most frequently targeted industries in the first quarter of 2018.
Government


The majority of attacks on government in Q1 2018 included malware use. Spyware (38%) and Remote Access Trojans (28%) made up the majority of malware. Phishing emails were the most common method of malware infection. For instance, in March 2018 PT ESC detected a phishing campaign involving an APT Trojan sent to government institutions. The APT Trojan in question was a modified version of SANNY spyware. Known since 2012, SANNY skillfully bypasses User Account Control (UAC) protections in Windows. The attackers created a macro document for each targeted company. Another group on the radar of Positive Technologies is ICEFOG, which has engaged in similar activity in the CIS and sent phishing documents with Fucobha malware. Vulnerability CVE-2017-11882 in Office Equation Editor was used to download the payload to the victim computer.
Most often, such phishing documents use published vulnerabilities. Therefore, if all updates are installed, accidental opening of such documents by an employee will not result in any system compromise.


Healthcare

Most attacks (65%) were intended to obtain sensitive information, specifically medical or personal data (44% and 36%, respectively). However, sometimes attackers are more interested in restricting access to data than stealing it. In January 2018, Hancock Health in the U.S. was hit by SamSam malware. The attackers encrypted the company's file system and demanded a ransom for the decryption key. Hospital operations came to a halt as staff had to enter patient medical data by hand. Despite having backups, the company estimated that restoring all systems would take too much time, and therefore decided to pay out the equivalent of $55,000.
Hospitals are regarded by many experts as a prime target for ransomware. The state of healthcare IT, along with the life-and-death consequences of system failures, makes administrators all too willing to pay ransoms to cybercriminals.

Finance


As usual, finance and banking companies tend to bear the brunt of attacks. Two thirds (64%) of attacks were aimed at direct financial gain. One third (36%) were intended to obtain information, most often account credentials (such as for internal bank systems) and bank records (such as client balances).
In Q1 2018, jackpotting attacks in the U.S. made news after resulting in theft of over $1 million from ATMs. Dressed as maintenance personnel, the criminals connected to an ATM with the help of a laptop, industrial endoscope, and mobile device. They then installed special malware (such as Ploutus-D), which allowed them to control the ATM and withdraw all of the cash inside.1 In the first quarter, PT ESC detected new phishing mailings from the Cobalt group targeting banks. These malicious attachments were generated using ThreatKit, with a vulnerability discovered in January (CVE-2018-0802).
Education


In attacks on educational institutions, the goal of attackers was usually to obtain data. Three quarters (75%) of attacks resulted in access to student or employee personal data, intellectual property, or credentials for education-related systems. University research can often have military, industrial, and other applications that make these institutions attractive to hackers.
In February, the U.S. Department of Justice announced charges against nine Iranian nationals, who are said to have participated in attacks on 320 universities in 22 countries to steal scientific documents and research data. The hackers used phishing to obtain the passwords for faculty email addresses and university systems. The information was distributed via Megapaper.ir and Gigapaper.ir, which allow freely distributing scientific works, and also may have been shared with the Iranian government.

Individuals


Ordinary people were the victims of 28 percent of attacks in Q1 2018. Malware featured in five out of every six incidents. Victim devices were most often infected with spyware (34%), cryptocurrency miners (27%), and adware (18%). The most common sources of infection were websites (33%) and official mobile app stores (25%).
The siren song of "free" has resulted in infection of those refusing to pay for content. Pirated copies of Fire and Fury, a book about Donald Trump, contained malware allowing access to the victim's computer. Russian-language Torrent site b-tor.ru bundled XMRig, a Monero cryptocurrency miner, with the files requested by users.
Search engines offer a way to spread phishing links, particularly in advertisements. In March, criminals placed a link to a phishing page on google.com; the link was a paid ad made to look as if it were from Amazon. After clicking the link, users were taken to a page imitating technical support for Windows or Mac computers. A pop-up window warned that the user's computer was infected with malware and personal information (such as credentials and credit card numbers) had been stolen. The user was then told to contact technical support and transfer money in order to prevent this information from getting out. In reality, the page belonged to scammers who had no access to the user's data.
What companies can do to stay safe
Use proven security solutions:
- Centralized update management
- Antivirus protection on all systems and endpoints, preferably with support for on-demand scanning by users of suspicious attachments prior to opening them
- SIEM capabilities, for timely attack detection
- Automated software audit tools, to identify vulnerabilities
- Web application firewall, as a preventive measure for websites
- Anti-DDoS services
Protect your data:
- Encrypt all sensitive information. Do not store sensitive information where it can be publicly accessed.
- Perform regular backups and keep them on dedicated servers that are isolated from the network segments used for day-to-day operations.
- Minimize the privileges of users and services as much as possible.
- Do not allow reuse of identical username–password combinations for multiple systems.
- Use two-factor authentication where possible, especially for authenticating privileged accounts.
Do not allow weak passwords:
- Enforce a password policy with strict length and complexity requirements.
- Require password changes every 90 days.
- Replace all default passwords with stronger ones that are unique.
Monitor and stay current:
- Keep software up to date. Do not delay installing patches.
- Test and educate employees regarding information security.
- Monitor the network perimeter for any new insecure resources.
- Regularly perform penetration testing to identify new vectors for attacking internal infrastructure and evaluate the effectiveness of current measures.
- Regularly audit the security of web applications, including source-code analysis, to identify and eliminate vulnerabilities that put application systems and clients at risk of attack.
- Track the number of incoming requests per second. Configure servers and network devices to resist typical attacks (including TCP/UDP flooding and database overloading).
- Filter traffic to minimize the number of network service interfaces accessible to external attackers.
Keep clients in mind:
- Improve security awareness among clients.Regularly remind clients how to stay safe online from the most common attacks.
- Urge clients to not enter their credentials on suspicious websites and to not give out such information by email or over the phone.
- Explain what clients should do if they suspect fraud.
- Inform of security-related events.
How vendors can secure their products
All of the preceding recommendations for companies ("What companies can do to stay safe"), plus:
- Implement a Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDL).
- Regularly audit the security of software and web applications, including source-code analysis.
- Keep web servers and database software up to date.
- Do not use libraries or frameworks with known vulnerabilities.
How users can avoid falling victim
Invest in security:
- Use only licensed software.
- Maintain effective antivirus protection on all devices.
- Keep software up to date. Do not delay installing patches.
Protect your data:
- Back up critical files. In addition to storing them on your hard drive, keep a copy on a USB drive, external disk, or a backup service in the cloud.
- Use an account without administrator privileges for everyday tasks.
- Use two-factor authentication where possible, such as for email accounts.
Do not use weak passwords:
- Set strong passwords at least eight characters long that include hard-to-guess combinations of letters, numbers, and special characters. Consider using a password manager to store, generate, and automatically enter all your passwords.
- Do not reuse passwords. Set a unique password for each site, email account, and system that you use.
- Change all passwords every six months, or even better, every two or three months.
Be vigilant:
- Scan all attachments with antivirus software.
- Beware when visiting sites with invalid or expired security certificates. Remember that all data entered on such sites is at particularly high risk.
- Pay close attention when entering passwords or making payments online.
- Do not click links to unknown suspicious sites, especially if a security warning appears.
- Do not click links in pop-up windows, even if you know the company or product being advertised.
- Do not download files from suspicious sites or unknown sources.
1 ATM attacks with such malware are detailed in the Positive Technologies report "Attacks against ATMs using GREENDISPENSER: organization and techniques."
Download PDF